大會發布 | 具身智能機器人十大發展趨勢?
時間:2025-08-15
2025世界機器人大會于8月8日開幕,開幕式上發布了《2025具身智能機器人十大發展趨勢》,以下為全文。
趨勢一
第一,物理實踐、物理模擬器與世界模型協同驅動的具身感認知。物理實踐是具身智能的本質,物理模擬器可以構建高保真的訓練環境,世界模型可以提供環境當中比較本質的內部特征。三者融合既可以保證豐富、有效、真實的環境,也可以用于訓練具身智能機器人與環境的接觸和非接觸交互的感認知能力,為其決策和控制奠定基礎。
趨勢二
第二,多層次端到端的具身決策。由多模態大模型啟發的,具有數理基礎的認知與規劃研究,與生命科學家的成果融合,并與實時的控制模塊融合,可以顯著增強具身智能機器人在非結構化環境下的泛化性和實用性。
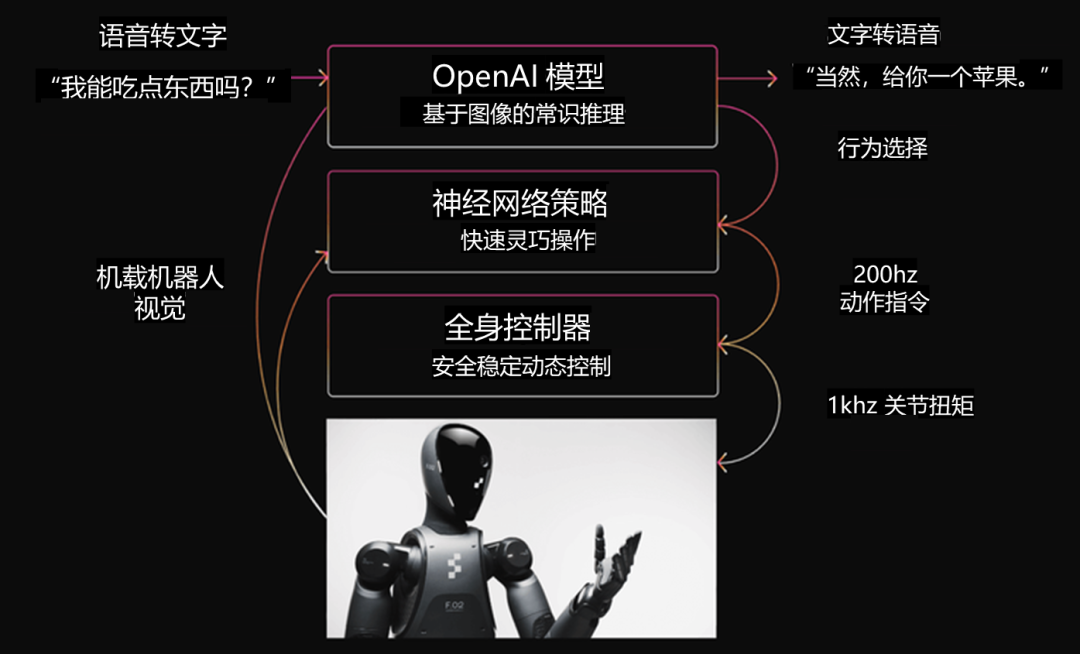
趨勢三
第三,從控制角度來看,可以融合模型預測、強化學習和生命科學的具身智能控制。一方面可以把模型預測控制的動態優化能力,把強化學習自適應決策融合起來,更進一步的與生命科學的冗余多環路控制機制相融合。這樣的話,可以更加讓具身智能機器人向人發展,實現具身智能的新控制,提升其在新環境當中的適應性和高性能。
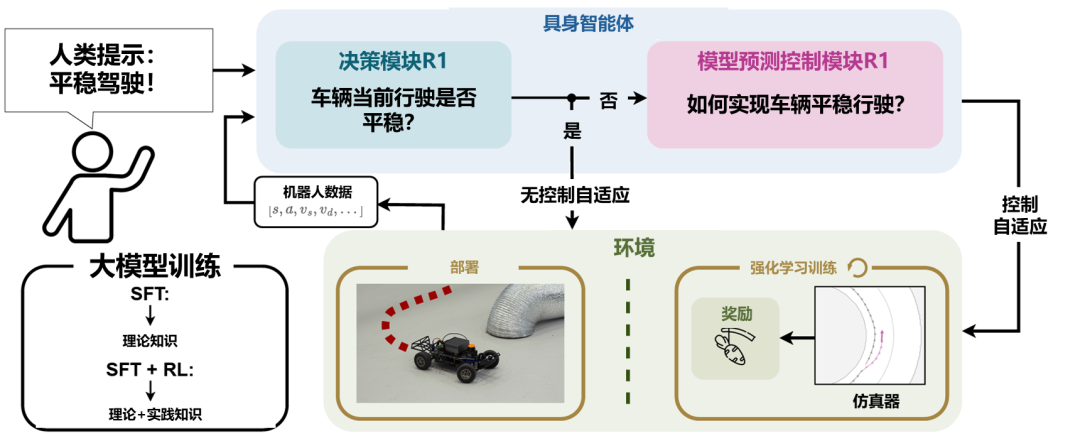
趨勢四
第四,生成式人工智能驅動的具身智能機器人設計。通過對于電機、減速器、驅動器、結構、連接件和材料的統一優化,同時與工材領域的科學成果相結合,在物理模擬器當中實現硬件與控制策略的協同優化,可自動探索任務中實現最優的具身智能的機器人設計。
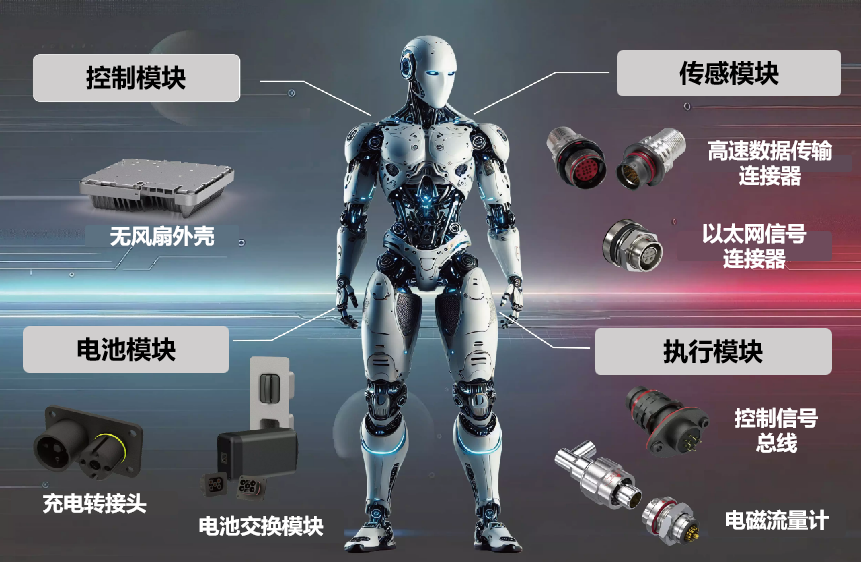
趨勢五
第五,高度協同與動態適配的具身智能軟硬件一致性。具身智能機器人需要軟硬件的一致性,在硬件開發的階段需預置適配算法的接口規范,在算法的設計當中又會內嵌物理約束,就是軟中有硬,硬中有軟,并且通過聯合仿真驗證,就是有軟有硬的情況下,讓系統更加保持一致,讓軟件模塊更加接近硬件,讓整體系統更加符合我們的軟硬件一致性的期望。
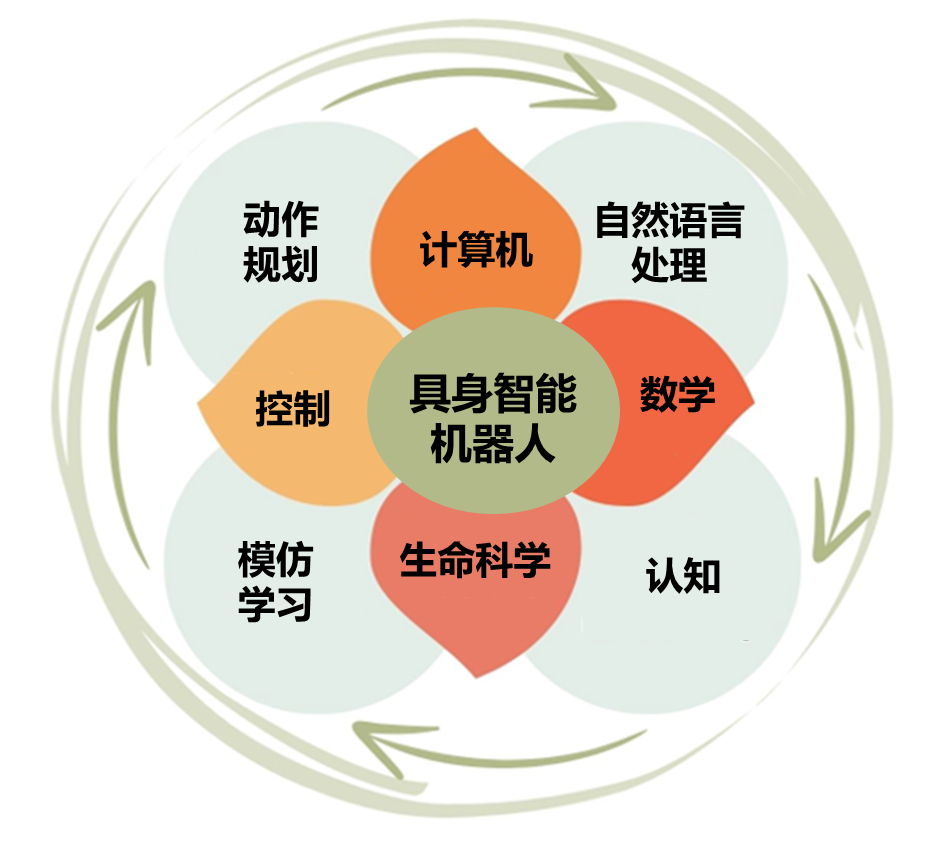
趨勢六
第六,具身智能機器人大工廠,在仿真環境當中實現自然語言交互、環境生成、機器人本體設計、決策-控制算法以及軟硬件一致性算法等研發,讓他們有機的結合在一起,并且反復進化。這樣的系統可以根據性能和需求實現快速設計和實現高質量具身智能機器人系統,為社會服務。

趨勢七
第七,具身智能大規模高質量數據集,基于物理實體采集與仿真合成構建大規模高質量具身智能數據集。這里高質量是一個關鍵,關于大規模,科研的期望是讓它規模要變小。同時可以顯著提升具身智能機器人的本體構型優化、多模態訓練效率及跨場景策略遷移能力。

趨勢八
第八,具身智能機器人集群及與人協同的發展,融合多智能體的協同機制,構建具身智能機器人集群。同時不斷提升具身智能機器人的安全性,及其與人的共情能力,讓具身智能機器人真正走向我們,真正走向人類,成為人類的朋友。

趨勢九
第九,跨學科的具身智能機器人開源社區。首先具身智能機器人的發展需要信息科學、工程與材料科學、數學物理科學、生命科學等多學科協作,將在全球范圍內聚集各領域的頂級科學家和工程人員,促進具身智能領域的技術探討,助力產業鏈的上下游深度融合和協作發展。
趨勢十
第十,面向具身智能機器人的安全評估與倫理建設,通過行為規范驗證、決策可解釋性分析,和數據安全性研究等,能夠確保建立面向具身智能機器人的安全評估體系和倫理規范。確保在復雜開放環境中決策的可靠性、可解釋性以及行為的安全性,這才使得具身智能機器人能夠走向我們的服務行業。

10 Trends of Embodied Intelligent Robots
TREND 1 Embodied Cognition Driven by the Synergy of Physical Practice, Physical Simulators, and World Models
Physical practice is the essence of embodied intelligence. Physical simulators construct high-fidelity training environments, while world models provide the internal characteristics of the environment. The integration of these three elements enables the creation of rich, effective and realistic environments for training embodied intelligent robots in perceptual and cognitive abilities regarding both contact and non-contact interactions with the environment, laying a solid foundation for decision-making and control.
TREND 2 Empowering Embodied Decision-Making via Multimodal Large Model
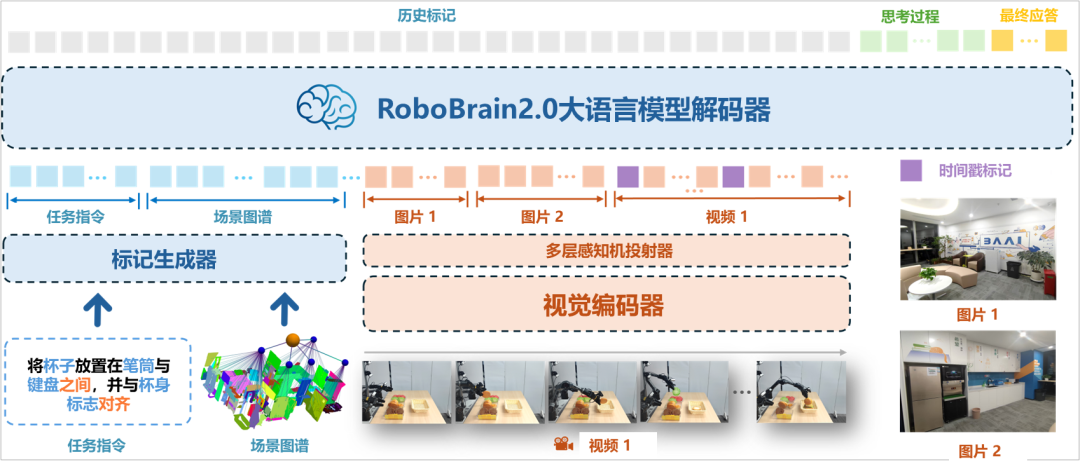
Multi-level end-to-end embodied decision-making: Inspired by multimodal large models, the research on cognition and planning with mathematical and physical foundations, integrated with life sciences and combined with real-time control modules, significantly enhances the task generalization ability of embodied intelligent robots in unstructured environments.
TREND 3 Embodied Intelligent Control via Integrating Model Prediction, Reinforcement Learning and Life Sciences
By integrating the dynamic optimization capabilities of model predictive control, adaptive strategies of reinforcement learning, and the redundant multi-loop control mechanisms from life sciences, an embodied intelligent robot control system is constructed to improve the generalization and adaptability of embodied intelligent robot control in dynamic environments.
TREND 4 Generative AI for Embodied Intelligent Robot Design
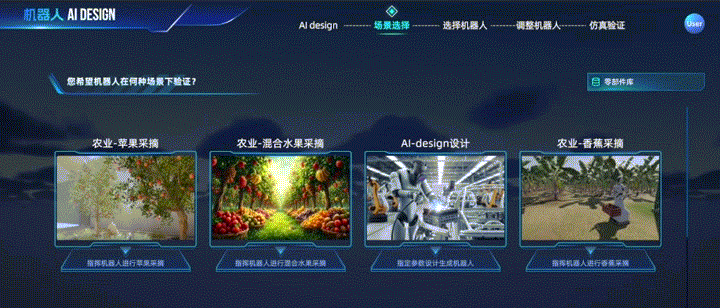
Generative AI-driven intelligent robot design realizes unified optimization of motors, reducers, drivers, structures, connectors, and materials. In combination with research and development technologies of robotic structure, it achieves co-optimization of hardware and control strategies in physical simulators, enabling automatic exploration of task-optimal embodied intelligent robot designs.
TREND 5 Highly Synergistic and Dynamically Adaptive Software/Hardware Consistency for Embodied Intelligence
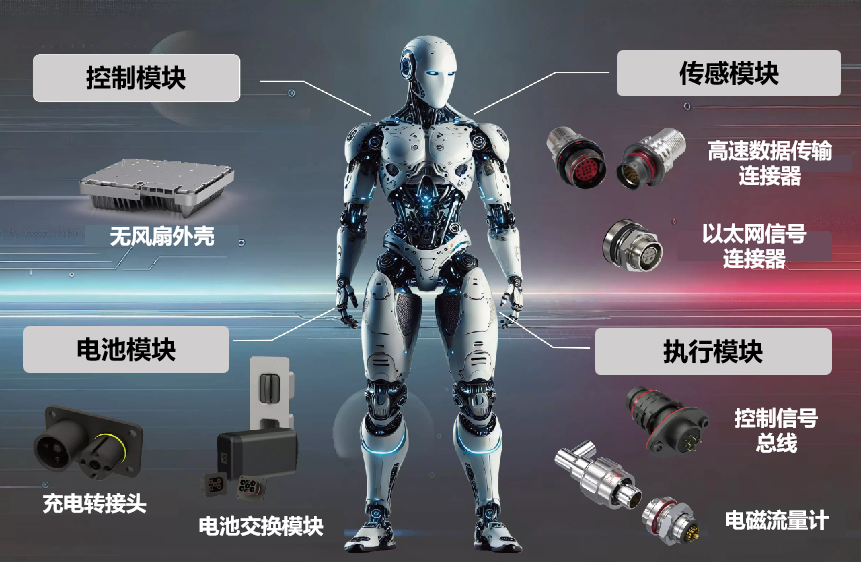
Embodied intelligent robots require consistent software/hardware co-design. By predefining interface specifications of algorithms during hardware development and embedding physical constraints of hardware into algorithm design, system-level consistency and optimization are achieved through joint simulation and validation.
TREND 6 “Manufactory” of Embodied Intelligent Robots

In the simulation environment, research and development efforts such as natural language interaction, environment generation, robot body design, decision-control algorithms, and software-hardware consistency algorithms are integrated into an organic whole, enabling rapid design and manufacturing of high-quality embodied intelligent robot systems according to specific performance and requirements.
TREND 7 Large-Scale and High-Quality Dataset for Embodied Intelligence

The construction of large-scale and high-quality datasets for embodied intelligence through physical entity collection and simulation synthesis can enhance embodied intelligent robots’ capabilities in morphological optimization, multimodal training efficiency, and cross-scenario policy transfer.
TREND 8 Advances in Embodied Intelligent Robot Swarms and the Collaboration with Humans
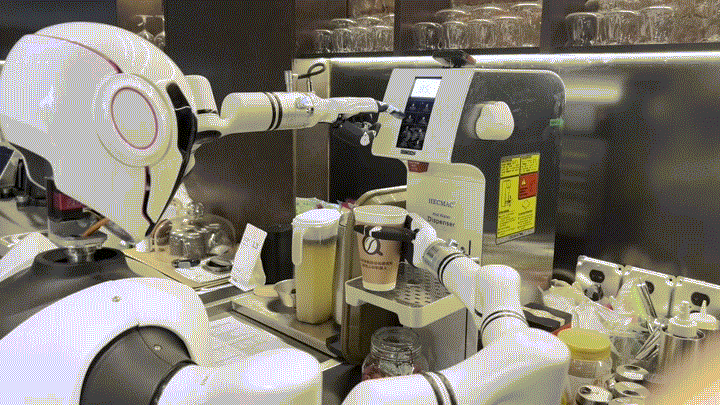
Integrating multi-agent coordination mechanisms to construct embodied intelligent robot swarms, while continuously improving the safety of embodied intelligent agents and their ability to empathize with humans, will facilitate such robots’ entry into human society and realize their integration with humans.
TREND 9 Interdisciplinary Open Community for Embodied Intelligent Robots
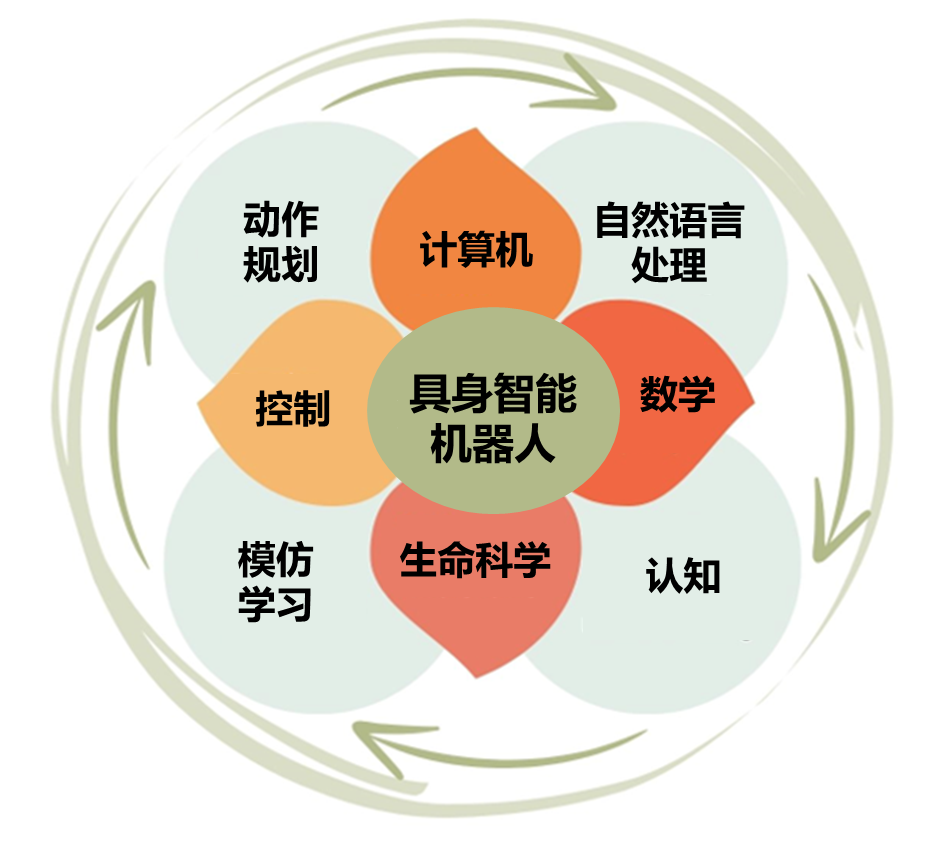
The development of embodied intelligent robots requires collaboration across multiple disciplines, such as information sciences, engineering and materials sciences, mathematical and physical sciences, and life sciences. This initiative will bring together experts and scholars worldwide to promote technical discussions in the field of embodied intelligence, and facilitate in-depth integration and collaborative development throughout the industrial chain.
TREND 10 Safety Assessment and Ethical Development for Embodied Intelligent Robots

Through behavior norm verification, decision interpretability analysis, and data security research, a safety assessment framework and ethical norms for embodied intelligent robots will be established to ensure decision reliability and behavioral safety in complex and open environments.
